- Explore Zinc
-
Platform
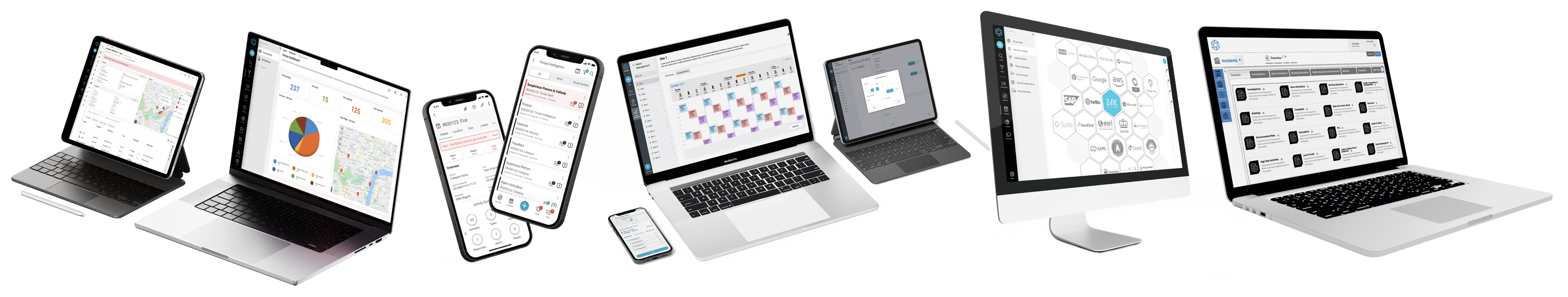
Delivering protection & assurance - an unparalleled platform designed for safety and security leaders who demand the highest level of control.
Explore -
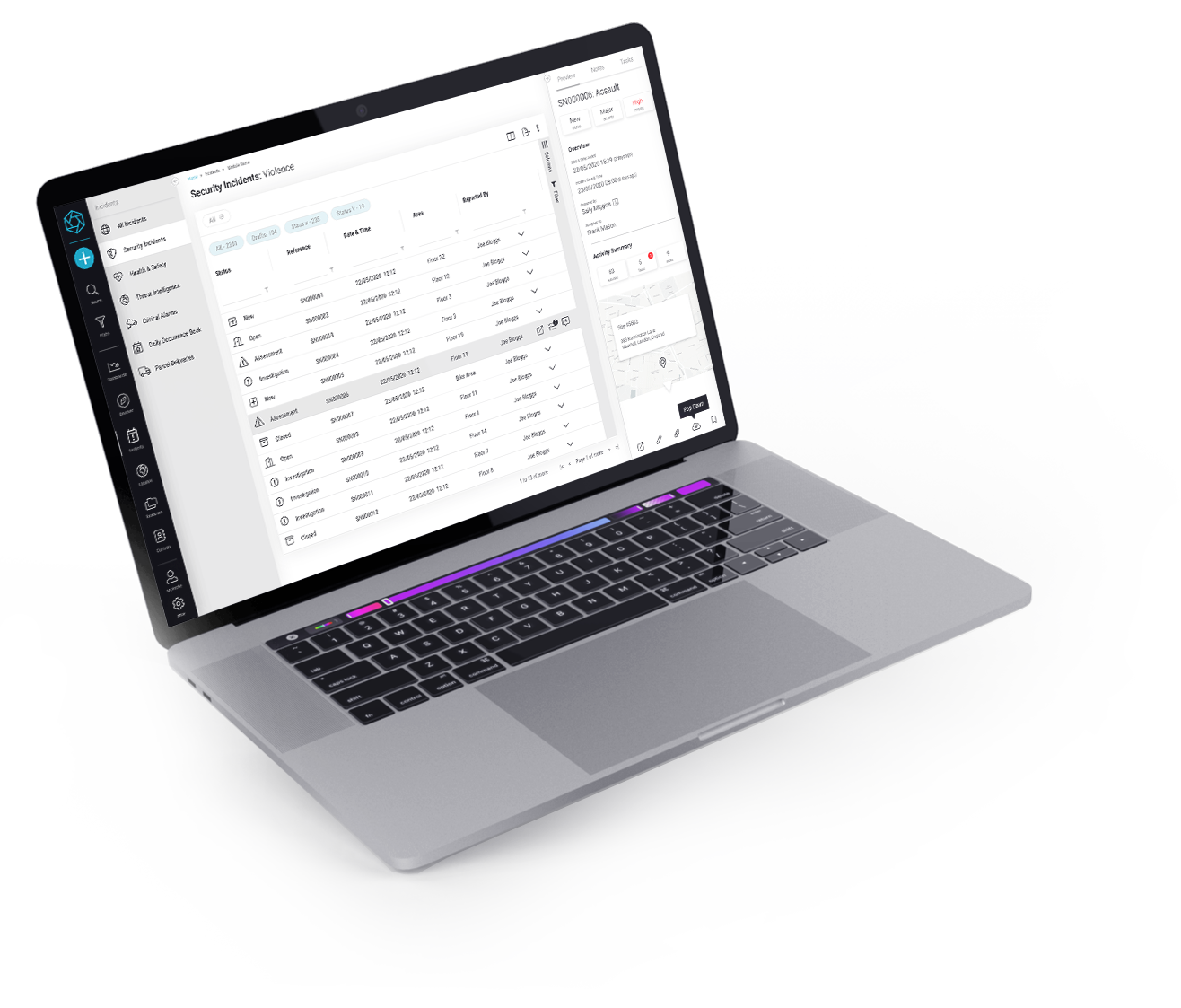
Incident & Critical Event Management
Navigate Crises,
Learn More
Maintain Continuity -
Mass Notification & Emergency Communications
Inform Quickly,
Learn More
Protect People -
Workplace Health & Safety Management
Promote Wellness,
Learn More
Prevent Hazards -
Compliance Activities & Patrol Management
Secure Operations,
Learn More
Ensure Compliance
-
Platform
- Sectors
-
Sectors
Across a number of sectors, our plaform is essential to enhancing operational continuity, asset protection, compliance and people safety of people.
Explore -
Iconic & tall buildings
Real estate portfolios
Venues & events
Studios & entertainment
-
Retail stores & supply chain
Critical national infrastructure
Security & FM service providers
Emergency responders
-
Sectors
- Resources
-
About
Like many tech titans, we also began our journey as a startup in humble garage - today, we are proud to protect some of the world’s leading organisations.
Learn More -
Product Hub
Feature Guide
Partner Program
Trust Centre
-
Learn
Industry Insights
E-Books
-
About
- About
- Contact us
- Demo Request






 +44 (0)1604 598989
+44 (0)1604 598989