Building Damage - covering; structural, roof, glazing, access, doors, shutters & barriers, external facade, fly tipping, property boundary, internal systems & utilities, signage and lighting
Building Systems - covering; fire systems, physical security systems, access control, CCTV, communication system failure, PAVA communications
Complaints - covering; maintenance issues, noise, cleanliness, hygiene & sanitation, structural & aesthetic issues, service & amenities, accessibility
Civil Unrest - covering; industrial action, protest & activism, civil disobedience
Data/Cyber Security - covering; data request, data protection, network & service disruption, targeted cyber exploits & manipulation
Fire - covering; fire, explosion
Mechanical & Electrical (M&E) - covering; HVAC, building maintenance unit (BMU), digital services, escalator failure, appliances, lift incident, lift entrapment, lighting doors, shutters & barriers, unsafe object, water leak, blocked drain, utilities
Missing Person and Vulnerable Person(s) - covering; missing minor (under 18), missing adult (18+), vulnerable person
Natural Disasters - covering; weather-related disasters, geophysical disasters
Suspicious Activity - covering; auditors, drone activity, hostile reconnaissance, suspicious behaviour, suspicious item
Terrorism & Domestic Threat - covering; bomb threat/attack, CBRN, drone, armed assaults, stabbing attacks, suicide bomber, attack, arson, human trafficking, vehicle as weapon / VBIED, kidnap, barricade/hostage, cyber terrorism, weapons
Theft - covering; burglary, fraud, robbery, theft, other loss
Unauthorised Access - covering; homelessness/vagrant, illegal gatherings, travellers, perimeter breach, unauthorised person on site, URBEX climbers, insecure area
Vehicles - covering; abandoned vehicle, car cruises, insecure, vehicle parking issue, road traffic collision, vehicle theft, vehicle damage
Violence & Unacceptable Behaviour - covering; alcohol or drugs, violence, unacceptable behaviour, anti-social behaviour, banning order
Edit and customise the existing incident types specific to your own requirements and processes.
Create your own incident types and workflows
Automatically integrate incidents from other systems to provide a single repository of all incidents across your business (see "APIs")
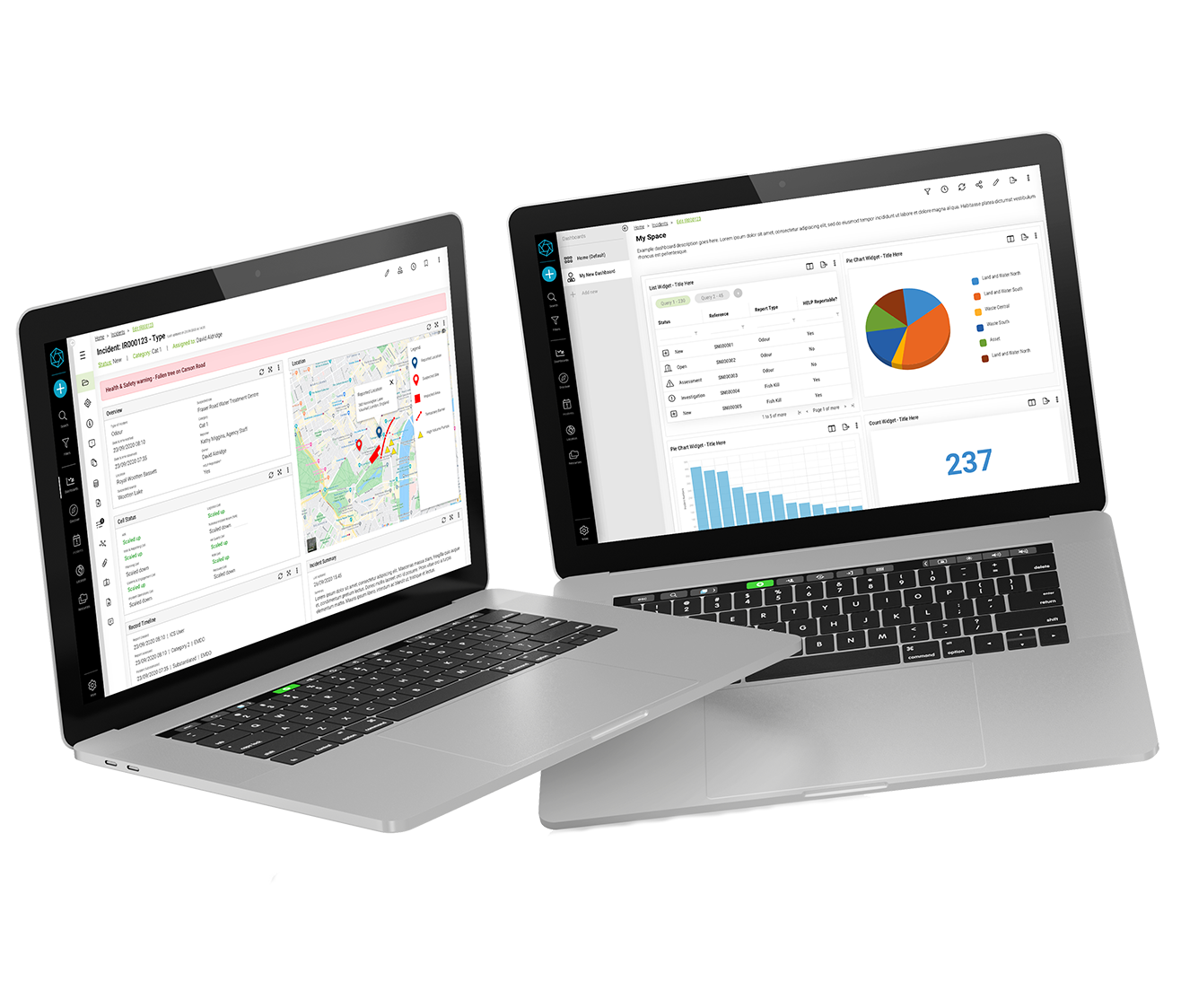
Three stages enabling the report to be structured: Report, investigate, analyse
Report - capturing of date / time, reporter details (internal - with a Staff lookup function, external/contractor or member of the public), location (with interactive mapping, layer selection, adding of points of interest or selection of existing sites), pre-made ‘details’ fields based on the selected incident type
Investigate - pre-made ‘assessment’ fields based on the selected critical event, involved parties (including reporter details, victims and injuries, witnesses, offenders/suspects and emergency services)
Analyse - pre-made ‘evaluation/conclusion’ and ‘analysis’ fields based on the selected critical event
Edit - complete changes, collate, consolidate and manage all evidence centrally ensuring it is handled securely and in a compliant way.
Assignment - triage and allocate responsibility of the alarms to individuals and teams - internal or 3rd party responders/keyholders.
Statuses - move the alarm report through the cycle through to closure.
Comments - two-way communication with responders, add notes, continuous commentary and narrative to the alarm report.
Mapping - view the alarm location, surrounding area, swop the view from map to satellite & activate layers for people/sites.
Criticality - set default priority & severity levels and manually escalate or deescalate alarms to keep teams informed.
EOP/SOP automation - automate & orchestrate pre-defined standard & emergency operating procedures by the auto-creation of tasks.
Files - upload media, files, CCTV & wide range of files to support an alarm either manually uploaded, from a mobile device or via the API.
Tasks - coordinate the planning & tracking of alarm response tasks to ensure designated actions are completed & deadlines are met.
Notifications - automatic or manually triggered alerts and notifications using a wide range of communication methods.
Responses forms - formalised responses, statements, checks, sign-offs, forms and processes can be setup and enforced.
Plot - add points, polygons & radius to the map with response forms to mark actions and additional locations i.e. damage, cordons etc.
Involved parties - capture of suspects, offenders, organised groups, victims, injuries, witnesses, vehicles and emergency services.
Linking - linking of alarms and other events, with configurable link relationships - allowing for a investigations to see the bigger picture.
Costs - Log all losses as a consequence of an alarm - from time-based costs, purchased resources to damages, stock losses etc.
Audit timeline - transparency of all updates, actions and activities conducted on an event, displayed in a clear timeline.
Data restrictions - management and control over user access & permissions defining which user group can access and manage.
Export - export the alarm details in a PDF format to print - PDF reports can branded and customised.
TV mode - for display on control rooms video walls and triage rooms for situational awareness and ongoing updates.
Data push - interface with 3rd party systems via API endpoints.
Search - powerful filtering facility & advanced query builder that allows users to customise search criteria, filter & interrogate data sets.
Analysis - map key metrics and unlimited reporting suites and dashboards using flexible widgets - add lists, counts, graphs & maps.
Iconic & tall buildings
Real estate portfolios
Venues & events
Studios & entertainment
Retail stores & supply chain
Critical national infrastructure
Security & FM service providers
Emergency responders





 +44 (0)1604 598989
+44 (0)1604 598989